ABSTRACT
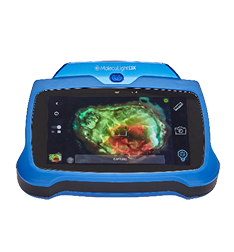
OBJECTIVE: Clinical evaluation of signs and symptoms (CSS) of infection is imperative to the diagnostic process. However, patients with heavily colonised and infected wounds are often asymptomatic, leading to poor diagnostic accuracy. Point-of-care fluorescence imaging (MolecuLight i:X, MolecuLight, Toronto, Canada) rapidly provides information on the presence and location of bacteria. This clinical trial (#NCT03540004) aimed to evaluate diagnostic accuracy when bacterial fluorescence imaging was used in combination with CSS for identifying wounds with moderate-to-heavy bacterial loads.
METHODS: Wounds were assessed by study clinicians using NERDS and STONEES CSS criteria to determine the presence or absence of moderate-to-heavy bacterial loads, after which the clinician prescribed and reported a detailed treatment plan. Only then were fluorescence images of the wound acquired, bacterial fluorescence determined to be present or absent and treatment plan adjusted if necessary.
RESULTS: We examined 17 VLUs/2 DFUs. Compared with CSS alone, use of bacterial fluorescence imaging in combination with CSS significantly improved sensitivity (22% versus 72%) and accuracy (26% versus 74%) for identifying wounds with moderate-to-heavy bacterial loads (≥104 CFU/g, p=0.002). Clinicians reported added value of fluorescence images in >90% of study wounds, including identification of wounds incorrectly diagnosed by CSS (47% of study wounds) and treatment plan modifications guided by fluorescence (73% of study wounds). Modifications included image-guided cleaning, treatment selection, debridement and antimicrobial stewardship.
CONCLUSION: Findings from this pilot study suggest that when used in combination with CSS, bacterial fluorescence may: (1) improve the diagnostic accuracy of identifying patients with wounds containing moderate-to-heavy bacterial loads and (2) guide more timely and appropriate treatment decisions at the point-of-care.